
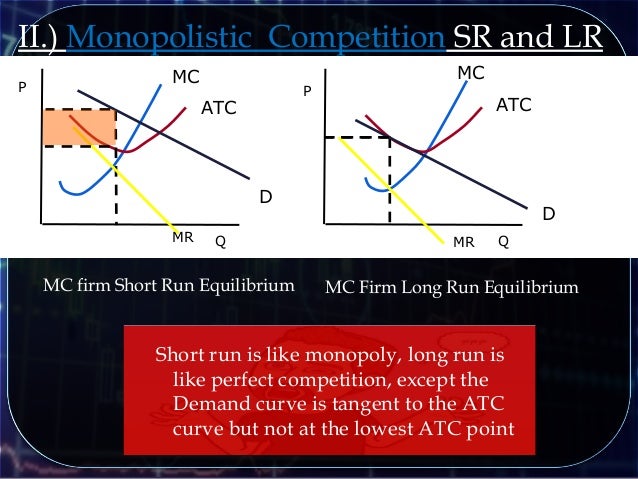

A residual demand curve is flatter than the market demand curve because individual firm demand is more elastic than market demand. The demand curve relevant to each firm in a monopolistic competition is called residual demand curve, a demand curve which shows the demand for product of one particular firm. This gives each firm some ability to set its own price. It is because due to the differentiated nature of products, they are not perfect substitutes for each other. The demand curve facing a firm in monopolistic competition is downward-sloping. Profit Maximization in Monopolistic Competition Markets which exhibit monopolistic competition include restaurants, hospitals, small retail outlets, etc. But monopolistic competition is also competitive because there are no barriers to entry and if the existing firms earn positive economic profits, new firms can enter the market easily thereby decreasing the market power of existing firms. Monopolistic competition is monopolistic in the sense that due to product differentiation each firm has some market power because due to its differentiated products even if it increases its price, its competitors can’t capture all of its market share. Monopolistic competition is a type of imperfect competition market structure in which a large number of firms produce differentiated products and there are no barriers to entry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
